To-Complete Performance Index (TCPI) in project management is a calculated metric that indicates the cost efficiency needed to achieve a project’s remaining work within the established budget.
Ever wondered how to know if your project is on track financially? Many project managers grapple with staying within budget while still delivering quality results. That is where understanding what is tcpi in project management becomes crucial.
This metric gives you a clear view of the efficiency required to complete the remaining project work. Think of it as a speedometer for project spending. It helps identify if you need to adjust resources or processes.
What is TCPI in Project Management?
Okay, let’s talk about TCPI in project management. It might sound like a complicated term, but it’s really a helpful tool to keep your projects on track. Think of it as a special calculation that tells you how well you’re managing your money on a project. TCPI stands for “To Complete Performance Index.” It’s a way of looking at how much money you have left and figuring out if you’re likely to finish the project within your budget.
Understanding the Basics of TCPI
Before we get into the nitty-gritty, let’s break down what TCPI actually means. Imagine you’re baking a cake. You have a recipe (your project plan) and a certain amount of ingredients (your budget). As you bake, you use up ingredients. TCPI helps you see if you’re using ingredients too quickly or if you have enough left to finish the cake as planned. It’s all about measuring how efficiently you need to work in the remaining part of the project to meet your budget goal.
Why is TCPI Important?
TCPI is important because it acts like a warning system. It helps you see problems before they become huge disasters. Without TCPI, you might not realize you’re overspending until it’s too late. This tool gives project managers a clear picture of what they need to do to stay within budget.
- It shows if you need to work more efficiently.
- It helps you adjust your plan if needed.
- It keeps you informed about your financial progress.
How is TCPI Calculated?
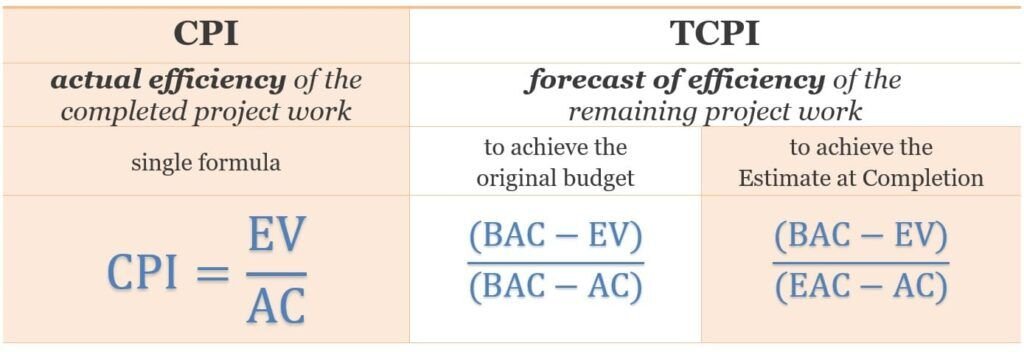
Now, let’s talk about the math part, but don’t worry, it’s not too complicated. TCPI is calculated using this formula:
TCPI = (Budget at Completion – Earned Value) / (Budget at Completion – Actual Cost)
Let’s break down each of these parts:
- Budget at Completion (BAC): This is your total planned budget for the whole project. Like, if your cake is supposed to cost $20 total to make, that’s your BAC.
- Earned Value (EV): This is how much work you’ve actually finished, in terms of money. If you planned to finish half the cake for $10 and you did, your EV is $10.
- Actual Cost (AC): This is how much money you’ve actually spent so far. Maybe you spent $12 instead of $10 for half the cake. That’s your AC.
So, the formula is basically showing us: what do you need to do, in terms of budget efficiency to achieve target. The remaining work you have to do (BAC – EV) divided by the money you have left (BAC – AC).
Let’s look at an example to make it clearer:
Example Scenario:
Let’s imagine you are building a birdhouse.
- Your budget (BAC) is $100.
- You’ve finished 60% of the work. This work you have finished was planned to cost $60 (EV).
- But, you’ve actually spent $75 to reach 60% completion (AC).
Now, let’s plug those numbers into the formula:
TCPI = ($100 – $60) / ($100 – $75)
TCPI = $40 / $25
TCPI = 1.6
What does this mean?
A TCPI of 1.6 means that for the remaining work to be completed within budget, you have to perform 1.6 times as efficiently. It’s a measure of required efficiency, not a real performance measure in the same way as CPI. It highlights the level of efficiency needed to stay on target.
Interpreting TCPI Values
Understanding what the TCPI number means is crucial. Here’s a simple guide:
- TCPI = 1: If your TCPI is 1, it means you’re on track. You’re spending money as planned, and you should be able to complete the project within budget, if you keep the current performance on the remainder project work.
- TCPI < 1: If your TCPI is less than 1, you’re doing better than expected. You have more budget than planned to complete remaining work. You’re spending less money than planned. Great work, keep it up!
- TCPI > 1: If your TCPI is more than 1, it’s a sign that you need to work more efficiently. You need to spend less money and work faster to finish the project within budget.
Let’s use our birdhouse example again. Since our TCPI was 1.6, that means we have to be very efficient with the remaining 40% of work. We need to spend money and use resources very carefully to avoid going over budget.
TCPI: An Example Table
Let’s consider a different scenario and put it in a table format to illustrate how the TCPI values change with project progress:
| Project Stage | Budget at Completion (BAC) | Earned Value (EV) | Actual Cost (AC) | TCPI | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | $500 | $0 | $0 | N/A | Project is at the starting point |
| Stage 1 | $500 | $100 | $110 | 1.04 | Slightly need to be more efficient for remaining work to achieve budget target |
| Stage 2 | $500 | $250 | $280 | 1.14 | Need to be more efficient in remaining work to achieve budget target |
| Stage 3 | $500 | $400 | $380 | 0.83 | Can reduce project efficiency. In remaining work, less efficient working can be afforded for the targeted budget. |
| Completion | $500 | $500 | $500 | 1 | Project completed at budget. |
TCPI vs. CPI (Cost Performance Index)
You might be wondering how TCPI is different from another common term in project management called the Cost Performance Index (CPI). Here’s the difference:
- CPI: CPI is a measure of your cost efficiency up to a specific point in time. It’s calculated as EV divided by AC (EV/AC). So, it tells you how well you’ve been spending money so far. For example, If CPI is greater than 1, it means you are spending less money that planned.
- TCPI: TCPI, on the other hand, is a future-oriented measure. It tells you how efficiently you need to work from this point forward to achieve the budget target.
Think of it this way: CPI is like looking in your rearview mirror to see how well you’ve driven. TCPI is like looking at the road ahead to see how you need to drive to reach your destination.
Using TCPI in Different Project Phases
TCPI can be used in different parts of your project, not just at the end. Using it at different stages provides unique advantages:
Early Project Stages
In the initial phase, TCPI can help establish budget trend. If initial TCPI calculation shows a value greater than 1, it gives an early indication of potential overruns, giving project managers the time to react to the budget issues before they become severe.
Mid-Project Stages
By the time you reach mid project phase, using TCPI calculation will help project managers assess progress and adjust strategies based on actual performance. It’s the perfect time to make changes to keep on track to achieve the project budget.
Late Project Stages
In the later phase of the project, TCPI can be used to manage any remaining budget. TCPI helps in making sure, even at the very end of the project, the budget goals are not compromised.
Steps to Use TCPI Effectively
To use TCPI effectively, follow these steps:
- Plan Carefully: Make sure you have a solid project plan and budget (BAC) before you begin. This makes the TCPI values more accurate.
- Track Progress: Keep track of how much work you’ve completed (EV) and how much you’ve spent (AC) regularly. Don’t delay this step.
- Calculate TCPI Regularly: Compute TCPI at regular intervals, at least weekly to get better budget progress visibility and take necessary actions in timely manner.
- Analyze the Numbers: Understand what your TCPI value means. Are you on track? Do you need to be more efficient?
- Take Action: If your TCPI is over 1, take action. Reassess your plan, find ways to reduce costs, or speed up work.
- Communicate: Keep your project team informed about the TCPI. Everyone needs to understand the importance of staying within budget.
Benefits of Using TCPI
Using TCPI offers several important benefits for project managers:
- Early Issue Detection: Helps identify budget problems early on, giving you time to fix them.
- Improved Budget Control: Allows you to manage your budget more effectively.
- Better Decision Making: Informs your decisions, helping you allocate resources wisely.
- Increased Project Success: Increases the chances of completing your project within budget and on time.
Limitations of TCPI
While TCPI is very useful, it’s also important to know what its limitations are:
- Accuracy of Data: TCPI relies on accurate budget and progress data. If the information you’re using is not accurate, the TCPI calculation will not be accurate, which will lead to wrong decisions.
- Focus on Cost: TCPI is mainly focused on cost performance. It may not consider other things that can affect project performance such as quality or schedule.
- Change Management: If the project scope or budget change, then TCPI may become outdated and will need recalculation to be relevant.
- Assumes Consistent Performance: TCPI assumes that the project team will continue working at the same rate in the future. That is not always the case, and future performance might be different.
Who Should Use TCPI?
TCPI is not just for big, complicated projects. It can be helpful for all types of projects. Here’s who can benefit from using TCPI:
- Project Managers: They can use TCPI as a tool to monitor budget performance.
- Team Leaders: They can use TCPI to keep their team focused and working efficiently.
- Stakeholders: They can use TCPI to know about budget progress and whether projects are on track.
- Anyone Managing Projects: From small home improvement tasks to large business projects, TCPI can help anyone keep their projects within budget.
TCPI in Agile Project Management
While TCPI is commonly used in traditional project management, it can be helpful in agile projects too. Here’s how:
- Iteration Planning: TCPI can help teams plan better in each iteration by showing how efficient the project has been in previous iterations.
- Budget Visibility: TCPI provides good visibility on the budget even in the agile project.
- Adaptability: Even with constant changes, TCPI can help the project team manage budgets effectively.
TCPI is useful in agile project to keep an eye on the overall budget, though agile teams focus on each iteration, using TCPI will make sure project budget does not go out of control.
Making TCPI Work for You
TCPI is a powerful tool if used in the right way. Here are some ways to make sure TCPI works for you:
- Train Your Team: Make sure everyone on the project team understands how TCPI works and why it’s important.
- Use Project Management Software: Modern project management tools can help you automate TCPI calculations, so that you don’t have to do it manually.
- Be Consistent: Keep measuring TCPI throughout your project. Consistency leads to better analysis and better project outcomes.
- Use With Other Tools: Do not solely rely on TCPI, instead, use it with other project management tools for a complete view of the project’s health.
TCPI is not a magic bullet that can solve all budget problems. It’s a tool that helps you manage your budget effectively. By understanding and using TCPI well, you can significantly improve your project’s chances of success. Remember, it’s not just about the numbers; it’s also about how you interpret them and what you do about them that counts.
In short, TCPI is a tool that helps you evaluate how much you need to work to stay within budget, it keeps you informed and helps you make good choices throughout the project.
PMBOK PMP – TCPI (To Complete Performnce Index) basics and scenarios
Final Thoughts
To-Complete Performance Index (TCPI) is a crucial metric for project management. It calculates the required efficiency to meet project goals. This index helps determine if a project is on track financially.
TCPI compares remaining work to the remaining budget. Project managers use it to adjust spending. Understanding what is tcpi in project management allows you to manage costs proactively.