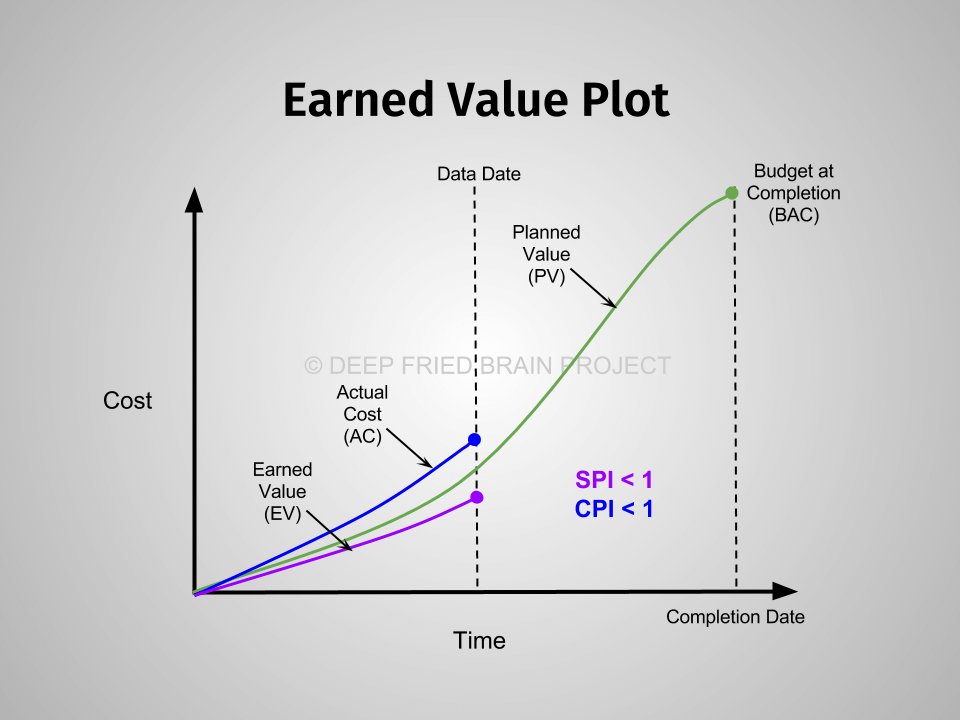
CPI in project management, or Cost Performance Index, is a ratio that measures the cost efficiency of a project. It calculates the earned value divided by the actual cost, indicating if you are over or under budget.
Ever wondered if your project’s spending is on track? That’s where understanding what is cpi in project management becomes crucial. This simple yet powerful metric provides a quick snapshot of your project’s cost performance. It’s a vital tool for project managers to monitor and control expenses.
A CPI value above 1 suggests you are under budget, while a value below 1 indicates overspending. Utilizing this index helps you take corrective actions early in the project lifecycle. This ultimately keeps project finances in check and aids in better project outcome.
What is CPI in Project Management?
Alright, let’s talk about something super important in project management: CPI. No, not the Consumer Price Index you might hear about on the news! In the project world, CPI stands for Cost Performance Index. Think of it as a report card for your project’s budget. It tells you how well you’re spending your money, and whether you’re getting the most bang for your buck. It’s a crucial metric that helps project managers keep things on track, avoid going over budget, and ultimately deliver successful projects.
Understanding the Basics of CPI
Imagine you’re building a really cool treehouse. You have a budget for lumber, nails, paint, and all that fun stuff. CPI is like a little helper that watches how much you’re spending compared to how much work you’ve actually completed. It’s not just about how much you’ve spent in total; it’s about how efficiently you’re using that money. Are you using your resources wisely? Or are you burning through cash faster than expected?
The CPI Formula
The formula for calculating CPI is actually quite simple:
CPI = Earned Value (EV) / Actual Cost (AC)
Let’s break down each part:
- Earned Value (EV): This is the value of the work you’ve finished so far. It’s like saying, “Okay, we planned to build this much of the treehouse, and we’ve actually built this much of it, and that work is worth this much money.” It’s based on your project plan’s budget for each task.
- Actual Cost (AC): This is the total amount of money you’ve actually spent on the project to date. It includes all your expenses, like lumber, nails, and maybe even snacks for the building team!
Once you have these two numbers, you simply divide the Earned Value by the Actual Cost to get your CPI.
What Does the CPI Number Mean?
The CPI number is your project’s score. It tells you how well your project’s expenses are being managed in relation to the work completed. Here’s the breakdown:
- CPI > 1: Great news! You’re under budget and ahead of cost! For every dollar you’ve spent, you’ve delivered more than a dollar’s worth of work. You’re being efficient with your funds. This is the goal!
- CPI = 1: You’re right on target! Your spending and the work you’ve completed are perfectly aligned, which indicates that project is running as per plan. You’re using your budget exactly as planned and you are where you need to be according to project’s progress.
- CPI < 1: Uh oh, you are over budget. For every dollar you’ve spent, you’ve delivered less than a dollar’s worth of work. This means your project is costing more than expected for the amount of work that’s been completed, and it might be time to investigate what is causing it.
For example, if your CPI is 1.2, it means that for every $1 you spent you have actually earned $1.20 in terms of work done. if your CPI is .8 then it means for each $1 you spent only earned 80 cents of value. Always aim for a CPI greater than 1.
Why is CPI Important in Project Management?
CPI isn’t just a cool number to track; it’s a very useful tool that can help your projects achieve success. Here’s why it’s so important:
Early Warning System
Think of CPI as an early warning system. It tells you when your project is heading toward a budget problem before it’s too late to fix. If you see a CPI consistently below 1, you know you need to take action. Ignoring a low CPI is like ignoring a red light – it will almost certainly lead to problems later.
Improved Budget Control
CPI gives you much better control over your project’s budget. You can see where you’re spending too much and where you might be able to save. By carefully looking at the numbers, you can make informed decisions about how to allocate your resources, thereby keeping your project finances in check.
Better Resource Allocation
By understanding your CPI, you can make informed decisions about how to allocate resources. Are you spending too much on certain tasks? Maybe there’s a way to do them more efficiently or use cheaper resources? CPI helps you see where to focus your efforts to stay on budget. It allows you to distribute the available resources to where they are most needed for maximum project value.
Accurate Forecasting
CPI doesn’t just look at the past; it also helps you predict the future. By tracking CPI trends, you can get an estimate of how much your project will ultimately cost. This helps you prepare for potential budget overruns and make adjustments as necessary to stay within budget. If your CPI is consistently trending downwards, that’s a clear indicator that you’ll need more funds to finish the project.
Communication and Transparency
CPI gives you an easy way to talk about your project’s financial health with your team and stakeholders. Instead of just saying, “We’re doing okay,” you can show them the numbers and explain what they mean. This promotes transparency and helps everyone understand the project’s financial status. Clear communication about the project financial status will ensure that all the stakeholder are on the same page and helps in better decision making.
Factors Affecting the CPI
Several factors can impact the CPI of your project. Understanding these can help you better manage your project’s financial health.
Scope Creep
Scope creep is when the project’s requirements grow over time. These changes can increase costs and make it harder to stay on budget, which in turn lowers your CPI. When you keep adding tasks and features to a project without adjusting the budget or timeline, it naturally throws off your cost performance.
Inaccurate Estimates
If your initial estimates for tasks were too low, you’ll likely end up spending more than planned. Having inaccurate estimates in your project plan can lead to an unfavorable CPI. The importance of spending adequate time in planning cannot be overstated.
Poor Resource Management
If your resources are not managed properly, then it can lead to spending more than planned and increase project costs. Inefficient allocation of resources, spending too much on certain aspects, and poor utilization of time will negatively affect the CPI.
Unexpected Risks
Unexpected problems or delays, like a broken tool or missing equipment, can cause extra costs. These surprises can knock your project off course and impact your budget and cost performance, leading to lower CPI.
Market Fluctuations
Changes in material costs or labor prices can also affect your project’s budget and CPI. If you had a fixed price estimate for lumber and the cost of lumber rises unexpectedly, it will certainly lead to an increase in cost. So it is very important to keep track of market fluctuations and account for them in your project plan and budgets.
Using CPI with Other Project Management Tools
CPI works even better when used with other project management techniques. Think of it as part of a bigger team of helpful tools. It plays a key role in the overall project management process by complementing other key project management metrics, giving project managers a more complete view of the project.
Earned Value Management (EVM)
CPI is a core part of Earned Value Management (EVM), which is a structured approach to project management that looks at three aspects: scope, time, and cost. EVM uses a variety of metrics to assess project performance, and CPI is one of the most important ones. EVM uses planned value, earned value, and actual cost to measure the project performance in comparison to the project baseline. When you use CPI with EVM, you get a full picture of where your project is financially.
Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
While CPI focuses on costs, SPI focuses on how well your project is sticking to its schedule. SPI compares the amount of work planned with the actual amount of work completed. Think of SPI and CPI as siblings. They each focus on different aspects of the project’s health: one measures time performance and another financial performance. Using both CPI and SPI gives you a much more rounded and clear picture of your project.
Variance Analysis
Variance Analysis is a technique used to assess the difference between planned and actual project parameters. CPI assists in variance analysis by highlighting the project costs differences from planned values. When project managers detect negative cost variance, they are able to initiate corrective actions, whether that means re-negotiation with vendors, or finding alternatives that are more cost effective.
Practical Examples of CPI in Action
Let’s look at a couple of real-world examples to make this even clearer. Imagine two different scenarios:
Scenario 1: The Website Redesign
You are tasked with redesigning a website for a client. Your plan is to spend $5,000 and have 50% of the work completed by the end of the first month.
- Earned Value (EV): $2,500 (50% of $5,000)
- Actual Cost (AC): $3,000
CPI = EV / AC = $2,500 / $3,000 = 0.83
This result tells you that your project is over budget. For every dollar you spent, you’ve only earned $0.83 worth of value. You need to check your expenses and find the reason for overspending.
Scenario 2: The Marketing Campaign
You are planning a marketing campaign with a budget of $10,000. Halfway through, the plan calls for 60% of the campaign to be finished, which is a value of $6,000.
- Earned Value (EV): $6,000
- Actual Cost (AC): $5,000
CPI = EV / AC = $6,000 / $5,000 = 1.2
In this case, your project is performing well. Your CPI of 1.2 means that for every dollar spent, you’ve earned $1.20 worth of work completed. You’re on budget or, even better, under budget!
Tips for Improving Your CPI
If your CPI is not where you want it to be, don’t worry! Here are some tips to help get it on track:
Realistic Planning
Make sure your initial estimates for each task are accurate and achievable. Do your research, talk to experts, and don’t be afraid to add some buffer for potential problems.
Careful Monitoring
Regularly check your project’s actual expenses and progress. The sooner you catch problems, the sooner you can start to fix them. Don’t wait until the very end to see if you are on budget, monitor it constantly.
Resource Optimization
Find ways to use resources more effectively. Are there less expensive resources you can use? Can you find ways to do things more quickly? Look for areas where you can reduce expenses without sacrificing quality.
Scope Management
Avoid scope creep as much as possible. If changes are needed, make sure they are properly evaluated and that the project budget and timeline are adjusted to reflect them. Stick to the planned parameters of the project as much as possible.
Continuous Improvement
After you’ve completed a project, learn from it. Evaluate what went well and what didn’t go so well. Use these insights to improve your planning and processes for future projects. Learn from your mistakes and do better next time.
Cost Performance Index (CPI) is a critical project management metric that helps project managers to stay within budget and to achieve project goals. By understanding its importance, and applying the recommended techniques, project managers can achieve project success.
The Schedule Performance Index – Key Concepts in Project Management from the PMBOK
Final Thoughts
Cost Performance Index (CPI) measures a project’s cost efficiency. It shows whether the project is over or under budget. A CPI above one indicates the project is under budget, while below one suggests it’s over budget.
The formula for calculating CPI is earned value divided by actual cost. This simple metric provides a quick overview of cost performance. Using CPI helps project managers take corrective action early.
Ultimately, what is CPI in project management? It’s a critical tool for monitoring and managing project expenses effectively. It allows for timely adjustments to keep projects financially on track.