To become a project manager, you often need to gain experience in project work, pursue relevant certifications, and develop strong leadership and communication skills.
Have you ever wondered how you become a project manager? It’s a career path that many find rewarding but it can be a bit confusing to know where to start. We will explore the necessary steps to navigate the route.
Many people have the right abilities but aren’t sure how to translate them into a PM role. Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered with information to help you understand the requirements. Getting into project management can be simpler than you think.
How You Become a Project Manager
So, you’re thinking about becoming a project manager? That’s fantastic! It’s a role that allows you to be a leader, a problem-solver, and a key player in making great things happen. Project managers are like the conductors of an orchestra, making sure all the different instruments (or team members!) play together in harmony to create a beautiful piece of music (or a successful project!). It’s not about just telling people what to do, it’s about helping them work together effectively and reach a common goal. This journey may seem daunting at first, but with some direction, you can take steps to begin your path.
Understanding the Role of a Project Manager
Before we dive into the how, let’s understand what a project manager actually does. They’re not just bosses; they’re facilitators, planners, and communicators. A project manager is in charge of planning, organizing, and directing projects. They ensure that projects are completed on time, within budget, and meet the set goals. They work with all kinds of teams and individuals to achieve success. Project management involves a variety of tasks, some of them include:
- Planning: Defining project goals, timelines, and resources.
- Organizing: Assembling a team, assigning tasks, and setting up work processes.
- Leading: Guiding the team, making decisions, and motivating members.
- Communicating: Keeping stakeholders informed of project progress and issues.
- Monitoring: Tracking progress, managing risks, and making adjustments as needed.
- Problem Solving: Addressing issues as they arise to keep the project moving forward.
A project manager’s role is dynamic and requires a diverse skill set. They are not just overseeing tasks; they are shaping the success of the project by providing structure and support to the team.
Building the Foundation: Essential Skills
Project management relies on a specific set of skills, both hard and soft. Let’s delve into the core competencies that will help you excel.
Hard Skills: Technical Competencies
These are the practical skills that you learn, often through education or training. They’re the tangible skills that allow you to do the job properly:
- Project Planning: Knowing how to break down a big project into smaller, manageable tasks and create a plan.
- Budgeting: Understanding how to create and manage a project’s budget.
- Scheduling: Learning how to create timelines and keep the project on track.
- Risk Management: Identifying possible problems and figuring out ways to deal with them.
- Technical Knowledge (in some fields): Having specific technical skills depending on the industry and project (for example, some level of understanding of software development for tech projects).
- Project Management Software: Knowing how to use tools like Jira, Trello, or Microsoft Project to help manage projects.
Soft Skills: People Skills
These skills are all about how you interact with others. They are equally important because a project manager works closely with different individuals to achieve shared targets:
- Communication: Being able to clearly explain things to your team, clients, and managers. This involves both speaking and listening.
- Leadership: Motivating and guiding your team, helping them do their best work. It’s about encouraging and supporting team members.
- Problem Solving: Thinking on your feet and coming up with ways to solve issues as they arise.
- Organization: Staying organized and keeping track of many different things at once.
- Time Management: Effectively planning and managing both your own and the team’s time to meet project deadlines.
- Teamwork: Being a great team player, understanding how to work well with different personalities, and collaborate toward a common goal.
- Conflict Resolution: Knowing how to handle disagreements within a team calmly and fairly.
- Negotiation: Being able to find win-win solutions when working with stakeholders with different priorities.
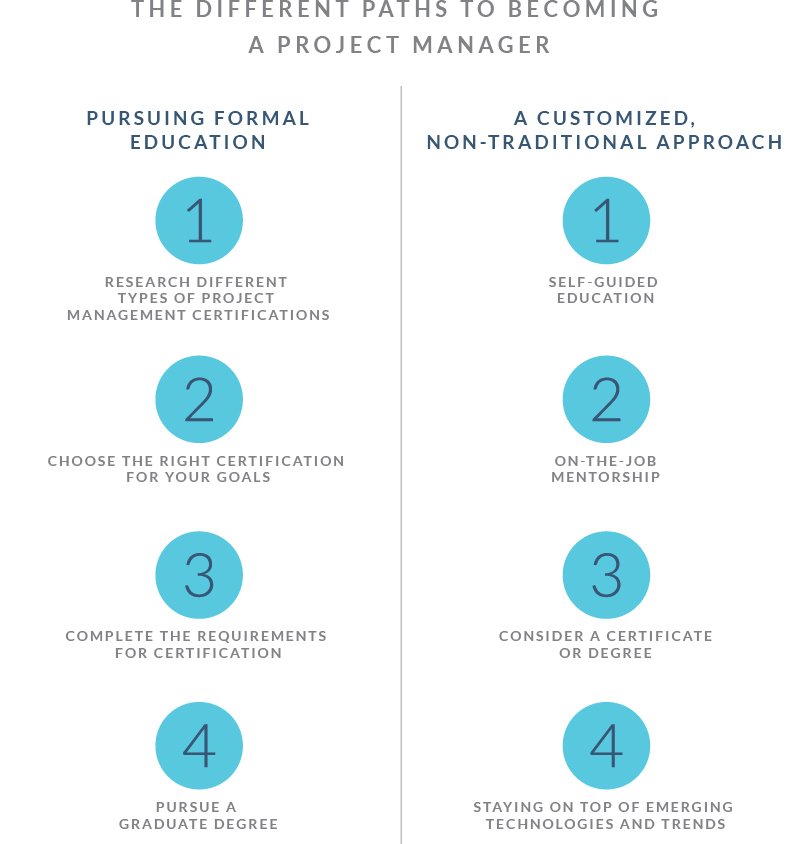
Education and Training Pathways
While a formal degree in project management is not always mandatory, it can give you a significant advantage. There are various educational paths one can take to prepare for the role:
Formal Education
- Bachelor’s Degree: Many people who are project managers have a bachelor’s degree in business administration, management, or a related field. This helps you learn basic business principles and develop necessary analytical skills.
- Master’s Degree: A Master’s degree in Project Management or similar provides more specialized knowledge and can propel career advancement in project management field.
Certifications
Project management certifications are like a badge that proves you have specific knowledge and skills. Many companies may even prefer candidates with certifications. Here are some of the popular and industry recognized project management certifications:
- Project Management Professional (PMP): The most common and sought-after certification by the Project Management Institute (PMI). Requires project management experience and passing an exam.
- Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM): Another certification from PMI, suitable for people with less or no project management experience.
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM): If you want to work in a team that uses Scrum, this is a good one to get.
- PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments): A popular methodology and certification, especially in the UK and Europe.
Online Courses and Workshops
There are numerous online courses available for learning project management through sites like Udemy, Coursera, and edX. These can be valuable for gaining foundational knowledge or developing specialized skills. Workshops provide practical training and hands-on learning experience. Some of them include:
- Project Management Fundamentals: Covering the basics of planning, executing, and closing projects.
- Agile Methodologies: Learning about the agile method of project management.
- Risk Management: Focused courses that teaches you to identify and handle risks.
- Project Management Software: Specific courses on how to use project management software like Microsoft Project, Jira, etc.
Gaining Practical Experience
Theory is important, but experience is equally vital. Here’s how to get hands-on project management experience:
Starting in Entry-Level Positions
- Project Coordinator: This entry-level job helps you get used to the project management world, often by assisting project managers and helping with tasks.
- Project Assistant: This role helps you learn the basics of how projects are handled.
- Administrative roles in project-based organizations: Even though not direct PM role, they provide important exposure to the project work environment.
Volunteer and Side Projects
If you can’t find a project management job right away, consider these options:
- Volunteer for projects: Look for non-profit organizations or community projects that need help managing their work.
- Start your own projects: Planning a personal event, a home renovation, or a community event is a great way to gain practical experience.
Shadowing or Mentorship
Learning directly from experienced project managers is super useful.
- Find a mentor: Ask an experienced project manager to guide you. A mentor can offer advice, share experiences, and help you navigate the process.
- Shadow experienced PMs: Offer to help or observe experienced project managers. Learning from seeing how they handle their day to day tasks is a great learning opportunity.
Networking and Professional Development
Building connections in the project management community and keeping your skills up to date is important for career growth.
Join Professional Organizations
- Project Management Institute (PMI): This is the big name in project management, providing certifications and many resources. Joining PMI gives you access to a community and lots of learning opportunities.
- Local Project Management Groups: Joining local groups connects you with other project managers in your area. This provides opportunities for learning and networking.
Attend Events and Conferences
- Project Management Conferences: These events bring together project management experts and help you learn about new trends and best practices.
- Webinars and Workshops: Taking part in online learning opportunities is a good way to stay informed and to gain specific project management skills.
Continuous Learning
- Read Industry Publications: Reading books, magazines, and websites about project management can keep your skills updated and expand your knowledge.
- Stay Updated on Tech: Project management is changing as technology changes. It’s important to stay updated with new tools and techniques.
Developing Your Project Management Style
As you grow in your journey as a project manager, you develop your unique way of handling projects.
Reflecting on Experiences
- Analyze Past Projects: Think about what went well and what didn’t. This helps you improve for next time.
- Seek Feedback: Ask your team and stakeholders about your performance and how you can do better.
Adapting to Different Project Types
- Small vs. Large Projects: Learn how to adjust your management style depending on the size and scope of the project.
- Different Industries: Project management principles apply across industries but learning industry-specific practices makes your job easier.
Finding Your Strengths and Weaknesses
- Knowing your strengths: Focus on what you do well and keep improving it.
- Working on weaknesses: Work to improve your areas that need improvement.
The path to becoming a project manager is one of continuous learning, both practical and theoretical. It involves gaining experience, developing key skills and staying updated with industry trends. It is a rewarding journey for anyone who likes to organize, lead, and solve problems.
How To Become A Project Manager
Final Thoughts
To become a project manager, you typically gain experience in various roles, building valuable skills. Seek out opportunities to lead small projects and volunteer for tasks requiring organization. Education, such as a project management certification, can also significantly boost your chances.
Experience is key, and you must actively learn practical skills. Networking can connect you with mentors. This way you navigate the path and understand how you become a project manager. Continuous learning is essential.