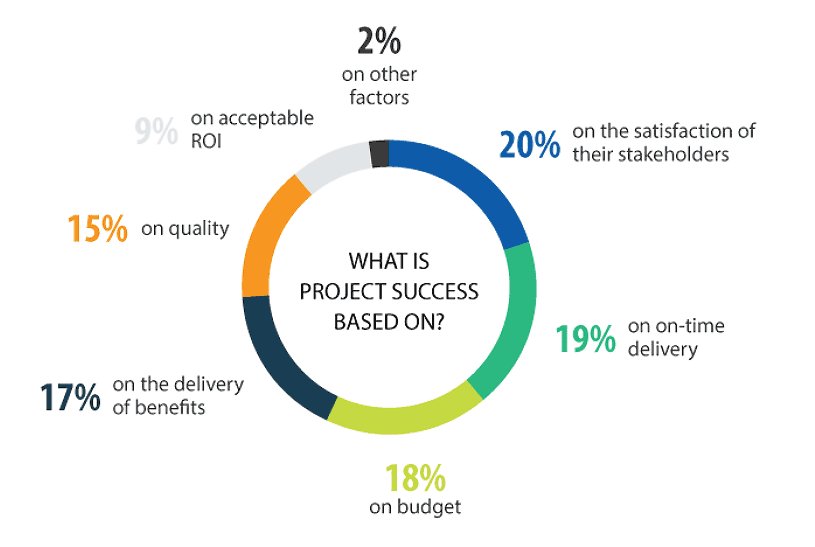
In project management, ROI (Return on Investment) is a key metric that measures how profitable or valuable a project is compared to its cost. It’s calculated by dividing the project’s net benefits by its total costs — helping teams understand whether the effort and resources invested are truly paying off.
Knowing what is ROI in project management is essential for making smart, data-driven decisions. It not only shows whether a project is financially viable but also helps prioritize initiatives that deliver the highest value. A strong ROI means the project is generating more benefits than expenses — a clear sign of success.
Project managers rely on ROI to compare potential projects, evaluate performance, and communicate results to stakeholders. In short, mastering this metric ensures every project aligns with the company’s strategic and financial goals.
What is ROI in Project Management?
Okay, let’s talk about something super important in the world of projects: ROI. You’ve probably heard the term before, maybe even in a video game or when your parents talk about their jobs. But what does it really mean when we’re talking about projects? Well, ROI stands for Return on Investment. Think of it like this: you put some effort and money into something, and you want to know how much you got back from it. That’s exactly what ROI helps us figure out in project management. It’s a simple way to see if the project was worth doing or if it didn’t make enough impact.
The Core Idea of Return on Investment
At its heart, ROI is a way to measure how profitable a project is. It answers the question, “Did we make money (or get some other benefit) from this project that was worth more than what we spent on it?” We’re not just looking at whether a project got finished; we’re looking to see if it was a good idea financially. This helps companies decide which projects are smart to do and which ones might be a waste of time and resources. It’s like a report card for projects!
Understanding the Basic Formula
Now, let’s get into how we actually calculate ROI. It’s a simple math problem. The basic formula for calculating return on investment is:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100
- Net Profit: This is the total amount of money (or other value) the project created, minus all the money it cost to do the project. It’s the money you ended up with after everything.
- Cost of Investment: This is the total amount of money that it cost to complete the project.
Let’s break it down with an example. Imagine you spent $100 on a lemonade stand, and you made $150. First, we figure out the net profit. That’s $150 (what you earned) – $100 (what you spent), which equals $50. So, you take your $50 profit and divide it by your $100 investment ($50 / $100 = 0.5). Then, we multiply that number by 100 to get a percentage: 0.5 100 = 50%. This means your lemonade stand had an ROI of 50%. For every dollar you spent, you got 50 cents back in profit.
Why is ROI Important in Project Management?
So why should project managers care about ROI? Well, it’s because it helps them make really good decisions. Here’s why ROI is so crucial:
- Justification of Projects: It shows why a project should be started in the first place. If a project has a low ROI (or a negative ROI), it might not be worth doing.
- Prioritization: When there are lots of projects competing for resources, ROI helps choose the best ones. Projects with higher ROI should get the most attention and support.
- Performance Measurement: ROI helps track how a project is doing over time. If the ROI is low, changes might need to be made.
- Stakeholder Communication: It provides a clear and easy-to-understand way to show stakeholders (like bosses and investors) the value of the project. Everyone wants to know that their money is being used wisely.
- Continuous Improvement: Analyzing the ROI of past projects helps teams learn and do better on future projects.
More Than Just Money: Understanding Intangible Benefits
Okay, so we’ve talked a lot about money. But sometimes, a project’s success isn’t just about dollars and cents. Many projects also provide things that are valuable but hard to put a price tag on. These are called intangible benefits, and they’re a big part of the overall return a project can give. Not all returns can be measured in dollar value, some examples are below.
Examples of Intangible Benefits
Intangible benefits can include:
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Happy customers are more likely to come back, which is good for business even if it’s hard to see the money right away.
- Improved Brand Reputation: A project that makes a company look good can attract more customers and partners.
- Higher Employee Morale: If a project makes employees feel proud and engaged, they’re more likely to work harder and stay with the company longer.
- Greater Efficiency: Projects that improve systems or processes can save time and resources in the long run, even if it’s not obvious in the short term.
- Better Innovation: Projects that help a company come up with new ideas or ways of doing things are valuable for future growth.
These types of benefits are very important even if they are not counted directly in our profit equation. While it might be harder to calculate the exact value of these kinds of benefits, we can try to assign a value to them or consider how these intangible benefits contribute to the overall project success.
Balancing Tangible and Intangible Returns
When evaluating a project’s ROI, we need to consider both tangible (money-related) and intangible (harder-to-measure) benefits. A project might not seem like a great financial investment at first glance, but it might be incredibly valuable because of the customer and employee benefit side. For example, a project focused on sustainability can create a more positive public image for a company that can bring more revenue in the future. Project managers use both kinds of benefits to paint a full picture of project success.
The Different Types of Costs in ROI Calculation
When we calculate ROI, it’s very important to have all of the costs included in our equation. There are costs that we can easily see and costs that are hidden. We must account for all of these costs to correctly calculate our ROI of the project.
Direct Costs
These are the costs we can see, and are easy to assign directly to the project. They are expenses that are incurred specifically because of the project. These include:
- Labor Costs: The salaries, wages, and benefits paid to the people working on the project.
- Material Costs: The costs of all of the resources (physical or digital) needed to complete the project.
- Equipment Costs: Expenses for buying or renting equipment for the project.
- Travel Costs: Money spent on transportation, lodging, and meals for project-related travel.
Indirect Costs
These are the hidden or the overhead costs that are not directly attributable to a specific project, but they need to be covered for the project to take place. These costs are often shared across multiple projects or activities within an organization. Examples include:
- Administrative Costs: Expenses for support teams like HR, finance, and IT.
- Facility Costs: Rent, utilities, and other costs associated with the office space or facilities used by the team.
- Marketing costs: Expenses used for the marketing of the project.
- Depreciation: The decrease in value of equipment or other assets used in the project.
Fixed and Variable Costs
Also keep in mind, that the cost can be either fixed or variable.
- Fixed Costs: These costs remain the same regardless of the project’s size, such as salaries for certain staff members and the rental of facilities.
- Variable Costs: These costs fluctuate depending on the project’s size or scope, such as material expenses and the fees of hourly workers.
Understanding all types of costs ensures that we have a complete picture of project expenditure and help accurately calculate ROI. Overlooking indirect or variable costs can create an overly optimistic view of a project’s profitability.
Calculating ROI for Different Project Types
ROI calculation can be different for various project types. While the core formula remains the same, the specific metrics used to measure the benefits and costs can vary. We will see how ROI might be calculated in various scenarios.
ROI in IT Projects
In IT projects, the costs often include software, hardware, and development effort. The benefits might be increased efficiency, decreased operational costs, and new revenue streams. Here is how that might look like:
- Cost: Costs include software licenses, hardware purchases, developer salaries, and project management costs.
- Benefits: Includes time saved through automation, reduced downtime, and increased sales through improved online platforms.
For instance, a company invests in new accounting software that costs $10,000, but it ends up saving the company $15,000 annually in labor costs due to time saved. The ROI calculation would be:
(($15,000 annual savings – $10,000 investment) / $10,000) x 100 = 50%. This would have a return on investment of 50%.
ROI in Marketing Campaigns
Marketing campaigns often focus on increasing brand awareness and generating leads. ROI is measured by the costs of advertising and the revenue that it generates. Key metrics include the cost per lead, customer conversion rates, and overall revenue generated by the campaign.
- Cost: Includes expenses for advertising space, creative services, salaries, and marketing tools.
- Benefits: Can include increased sales, improved brand recognition, and more customer engagement.
For example, a business spends $5,000 on a social media campaign and generates $10,000 in sales. The ROI is (($10,000 revenue – $5,000 cost) / $5,000) x 100 = 100%. This campaign has an ROI of 100%.
ROI in Construction Projects
Construction projects are capital-intensive and typically have long timelines. ROI is calculated by comparing the building costs to the projected revenue (like rent) or increased property value. Here’s what it looks like:
- Cost: Includes all the expenses for materials, labor, permits, and equipment.
- Benefits: Includes revenue generated through renting, or the increase in value of the property after the project is completed.
Imagine a company builds an apartment building for $1 million, and after 1 year the building generates $1.2 million in rental income. The ROI of this project is (($1,200,000 – $1,000,000) / $1,000,000) x 100 = 20%. So the ROI is 20%.
ROI in Product Development
In product development, the project cost is compared against the revenue generated from product sales. This involves expenses for design, prototyping, testing, and manufacturing.
- Cost: Includes design costs, prototyping costs, testing costs, and manufacturing expenses.
- Benefits: Include the revenue from product sales and long-term sales growth.
A new product is launched with an investment of $50,000, and in the first year generates $100,000 in sales. The ROI is (($100,000 – $50,000) / $50,000) x 100 = 100%. This product has an ROI of 100%.
Using ROI to Make Informed Decisions
ROI isn’t just a number to calculate and then forget about. It is a vital tool for project managers, stakeholders, and other team members. How should we use the information that we get from calculating the ROI?
Project Prioritization
When multiple projects are competing for resources, the use of ROI can give valuable information to allow better decision-making. If a project promises a high ROI, it should receive a higher priority. This approach ensures that the organization invests in projects that generate the most value.
Resource Allocation
ROI helps project managers allocate resources more effectively. By understanding which projects offer higher returns, project teams can use their resources for the best possible outcome. Projects with a lower return might need to have their resources reduced to maximize the overall profitability of the business. The goal is to ensure that money, time, and other critical resources are used wisely.
Performance Evaluation
Regularly evaluating project ROI helps teams see how well their projects are performing. It helps them find ways to make improvements. If a project isn’t doing well, the project team can investigate and fix it. This evaluation helps the team learn and do better with future projects. It provides valuable insight into areas that need improvement to make sure that the resources are being put to use most efficiently.
Communication with Stakeholders
ROI can effectively show to stakeholders how a project is creating value. Stakeholders include investors, bosses, and other team members, all of whom want to see that resources are used effectively. A clearly explained ROI calculation ensures that everyone understands the project’s profitability and strategic importance. Transparent reporting builds confidence and trust. When the stakeholders know how their money is being used, it will make them more supportive of the project.
Challenges in Calculating ROI
While ROI is a powerful tool, calculating it can sometimes be tricky. There are several obstacles that can make the process difficult.
Difficulty in Quantifying Intangible Benefits
One of the biggest challenges in calculating ROI is the difficulty of putting a numerical value on intangible benefits like better customer satisfaction or employee morale. How much is a happy customer worth? That’s hard to measure. Project managers have to use estimates or proxies to figure out these kinds of values, but it’s not always precise.
Data Inaccuracy
ROI calculations are only as good as the information used to calculate it. If project cost or revenue data isn’t accurate, ROI calculations will be off. Data issues can come from bad tracking systems or human error when reporting project-related expenses. Ensuring data accuracy requires using reliable tracking tools, regularly reviewing data, and following strict reporting protocols.
Time Lag Between Investment and Return
The return on some projects can take a very long time to realize. These include long-term projects like infrastructure development or research and development. The return might not be immediate or short term, which can make it difficult to calculate ROI in the short term. Project managers must understand that the benefits can accrue over a long time and that sometimes they might need to make long-term estimates.
Changing Market Conditions
ROI predictions can be affected by changes in the market. External factors like changes in the economy or new competition can affect the success and profitability of a project. Project managers need to be aware of these possibilities and be prepared to adapt to changing market dynamics to ensure they get a good return on their investment. They may have to adjust ROI calculations with market changes to have an accurate picture of the projects profitability.
Estimating Future Revenues
Predicting the future revenue from a project is always challenging. You can take a guess, but you might be wrong. Projects can take a different path than what was originally planned. Revenue projections might be too optimistic, which can lead to an inaccurate assessment of ROI. Realistic revenue forecasting, based on market trends and good data, is needed for accurate results.
Tips for Improving ROI in Project Management
Now that we know what ROI is and how to calculate it, here are some useful tips for ensuring that the projects have the best chance for a high return on investment.
Thorough Planning
Good project planning is key to success. A well-thought-out project plan will have clear goals, timelines, and resource allocation. Understanding the project scope, potential risks, and resource requirements helps make sure that the project is done within the budget and timeframe, increasing its profitability.
Effective Risk Management
Unexpected events can affect a project’s budget and time. Having a plan to handle these risks helps reduce any negative impact. Project managers should assess the risks of a project, create plans to avoid them, and be ready to adapt if things change. Addressing these risks can avoid potential losses and keep the project running well.
Proper Resource Allocation
Make sure you are using the best resources for each job and keep an eye on spending. Resources should be used efficiently, and unnecessary costs should be avoided. Project managers need to carefully select the resources and make sure they are being used effectively to optimize ROI.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Don’t just set a plan and then forget about it. Monitor the project progress regularly, and evaluate if it is on track. Tracking project performance with regular check-ins helps identify potential issues early so that changes can be made quickly. Tracking progress and implementing improvements help to make sure the project is successful and profitable.
Utilizing Project Management Tools
Project management software can help to streamline project management processes, which helps in saving both time and money. Project management software helps with planning, resource allocation, and communication. Using these tools can improve project efficiency and boost its return on investment. These tools will make the project more organized, and keep the team on track.
Stakeholder Involvement
Keeping the stakeholders involved and informed throughout the project helps keep everyone on the same page. Stakeholders can give valuable feedback that can improve a project’s value. When people are more involved, there is a better likelihood of a successful and profitable project. Stakeholder support is very important to the success of any project.
By carefully planning, managing risks, allocating resources, and communicating with the stakeholders, project teams can increase the likelihood of project success and achieve a better return on investment. Remember, ROI is not just about money, it’s about the value a project provides.
Understanding ROI is essential for successful project management. It provides a way to measure the value of projects, helping to make informed decisions about which projects to pursue. While ROI calculation might have challenges, project managers that know how to use ROI can prioritize projects, allocate resources, and communicate with stakeholders effectively. Considering both tangible and intangible benefits will give a clear picture of the project’s overall value. By using the best practices, project teams can improve the return on investment for the organization’s efforts.
What is ROI – Return on Investment?
Final Thoughts
Project ROI measures the profitability of your initiatives. It helps you assess if a project is worth pursuing by comparing its gains to its costs. A positive ROI indicates good financial performance.
Calculating the project ROI guides investment decisions and resource allocation. You can analyze different project options effectively. Remember that a higher ROI generally signals a better investment.
In conclusion, what is ROI in project management? It’s a key metric reflecting a project’s financial return. This value enables project managers to make data-driven decisions.